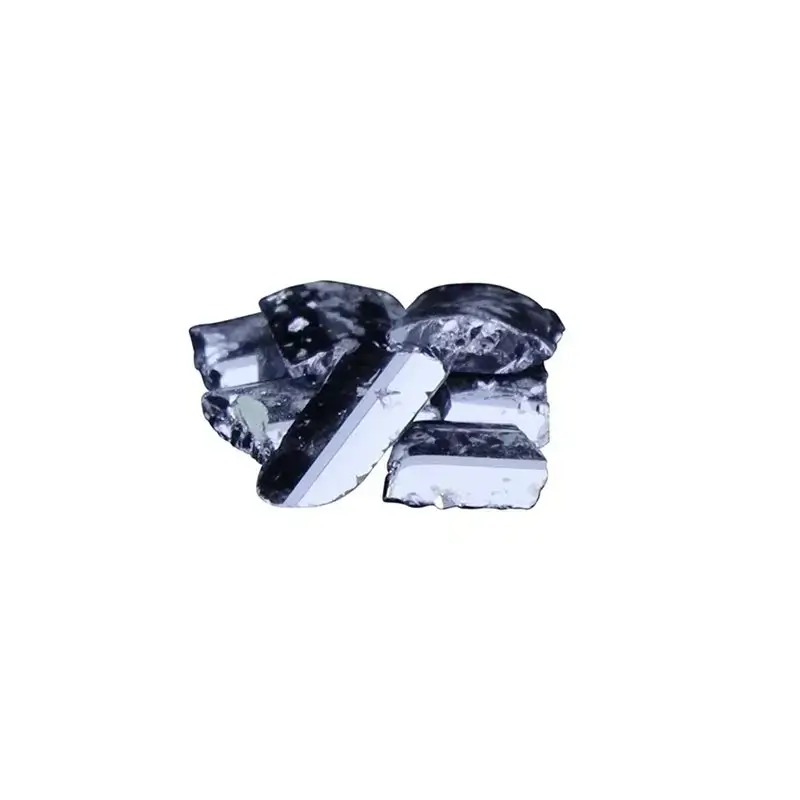
Europium
Europium is a soft, silvery rare earth metal known for its strong luminescent properties. It is mainly used in phosphors for LED lights, TV screens, and fluorescent lamps, producing red and blue colors. Europium is also used in anti-counterfeiting features in Euro banknotes. Available in powder and oxide forms.
Gallium
Gallium Metal is available in high-purity grades of 4N (99.99%) and ultra-high purity 7N (99.99999%). It is offered in granule or shot form to suit various industrial applications. Packaging options include 100 grams, 500 grams, and 1000 kilograms, based on customer requirements. Gallium is widely used in the semiconductor industry, solar cell production, and as an N-type dopant in electronics.
Praseodymium
Praseodymium is a soft, silvery rare earth metal belonging to the lanthanide series. It is known for its excellent magnetic, electrical, & optical properties. Praseodymium is commonly used in making strong permanent magnets, colored glass, ceramics, & in high-temperature applications such as aircraft engine parts.
Samarium
Samarium is a silvery rare earth metal belonging to the lanthanide series. It is best known for its use in Samarium-Cobalt (SmCo) permanent magnets, which are powerful and heat-resistant. Samarium is also used in nuclear reactors as a neutron absorber and in specialized optical glasses & ceramics.
Selenium
Selenium is used for digital X-ray sensor in the medical diagnosis equipment such as mammography, and is now focused for the application of CIGS (Cu/In/Ga/Se) compound solar cell. The ability to precisely dope with such elements like As, Cl, Te and alkarine metals in the unit of ppm to % order and stable and constant supply are the remarkable advantages of the technology.
Silver
Silver is a soft, white, lustrous metal known for its highest electrical and thermal conductivity of all elements. It is widely used in jewelry, coins, electronics, photography, and solar panels. Silver also has strong antibacterial properties, making it useful in medical and hygiene applications.
Yttrium
Ytterbium Metal (Yb) is supplied with a high purity of Yb/TREM 99.9% and a total rare earth oxide (TREO) content of ≥99.5%. The metal is available in chunk form, with individual pieces ranging in size from 7 to 10 mm. To preserve its quality and prevent oxidation, the product is securely packed in vacuum-sealed packets. Each bottle contains 250 grams of Ytterbium metal.